E/E Systems We Are Familiar With
We ensure the safety of your products. With expertise and standards.
MRI Scanner
Die Magnetresonanztomografie nutzt ein starkes statisches Magnetfeld von typisch 1,5 Tesla und ein hochfrequentes magnetisches Wechselfeld bei der Larmorfrequenz von rund 64 Megahertz, um die Spins der Wasserstoffkerne aus ihrer Ausrichtung zu kippen.
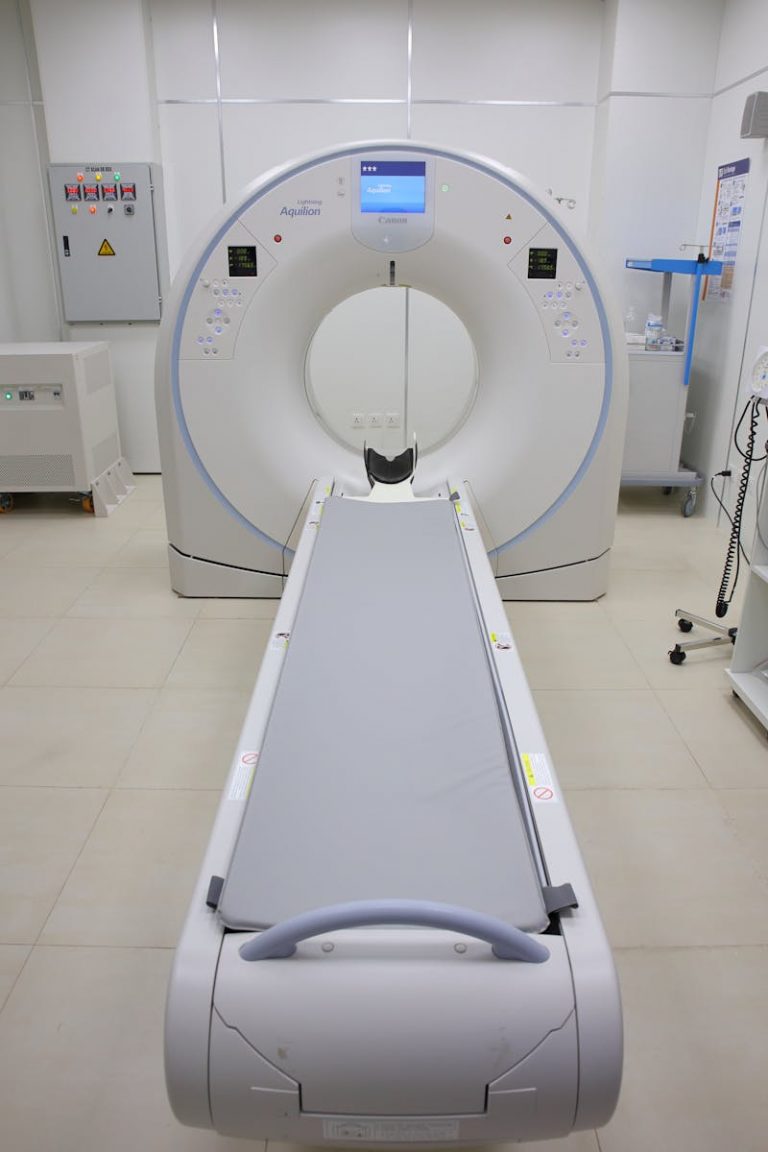
Nach dem Abschalten des Wechselfeldes beginnen die Spins im statischen Magnetfeld frei zu präzedieren. Beim Rückkehren in den Gleichgewichtszustand entsteht je nach Gewebe für 30 ms bis 2000 ms an den Empfangsantennen ein sehr schwaches Signal von ungefähr minus 120 dBV. Mit verschiedenen Ansteuerungen des Wechselfeldes wie Spin Echo, Gradient Echo, Inversion Recovery lässt sich wasserstoffhaltiges Gewebe messen und bildgebend je nach Abklingdauer unterscheiden. Mit der Ausrichtung des statischen Magnetfeldgradienten lässt sich die darzustellende Schnittebene frei wählen.
- HF receiving coils for the head and spine
- patient couch
Li-Ion Energy Storage Systems (ESS)
Li-ion energy storage systems pose significant safety risks such as fire or explosion in the event of a fault. For this reason, the battery management system (BMS) must be designed in accordance with internationally recognized functional safety standards such as IEC 61508 or ISO 13849.

The safe design of lithium-ion storage systems is not an option, but a necessity. It is essential for risk minimization, certification, and customer confidence.
- Battery Management Systems
- Inverter
Battery Electrical Vehicles (BEV)

The BMS in a battery electric vehicle monitors, controls, and protects the high-voltage battery by regulating parameters such as state of charge (SoC), temperature, and cell voltage to ensure maximum performance, safety, and battery lifespan.
- Battery Management Systems
- Inverter
Sensors
RADAR, LiDAR, and GNSS sensors enable vehicles to perceive their surroundings, detecting objects, mapping terrain, and determining position in real time to support fast, reliable decision-making. In Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) each play distinct and complementary roles to leverage their strengths and compensate for individual weaknesses.

- RADAR
- LiDAR
- GNSS (GPS, GLONASS)
Automotive Steering

- Electric Power Steering (EPS)
- Rear Axle Steering (RAS)
Electric power steering (EPS) and rear-axle steering (RAS) improve driving dynamics through greater steering precision, better maneuverability, and better integration with ADAS functions.
With safety-related implications, our expertise covers the entire development life cycle:
- Concept phase, including identification of critical driving maneuvers
- System, hardware, and software development
- Performance testing and safety validation with everyday drivers
Chassis Systems
Chassis control systems optimize the balance between ride comfort and driving stability by continuously adapting to road conditions and dynamic driving scenarios. These systems reduce the pitching, rolling, and bouncing of the body, for example, ensuring a smoother ride and improved handling.

- Adaptive Suspension
- Active Suspension
- Air Suspension
- Double Clutch System
However, due to their direct influence on vehicle dynamics, failures in chassis control systems can pose significant safety risks, potentially leading to vehicle instability or loss of control. To mitigate these risks, we bring extensive expertise in:
- Hardware and software development for safety-critical control systems
- In-depth understanding of vehicle dynamics and driver behavior
- Functional safety engineering and validation under real-world conditions
